Cervical osteochondrosis is a type of dystrophic change in the intervertebral discs in the neck.
It affects not only the discs themselves, but also the vertebrae, soft and cartilaginous tissue. The main feature of the cervical region is that its vertebrae do not have the most reliable structure compared to other regions, which makes this region very sensitive. The vertebrae are located close to each other, as well as to the arteries that feed the human brain.
If there is a displacement of the spine, then there is a high probability of compression of the nerve ligaments and arteries, which will inevitably lead to the formation of a hernia between the vertebrae and the protrusion, ie. changes in the structure of the vertebral disc.
What is this?
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (Osteochondrosis) is a degenerative-dystrophic damage to the intervertebral discs, which results in damage to the discs themselves, the vertebrae and joints of the spine, and a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs. . If left untreated, the disease progresses and can cause headaches, poor blood circulation, and even a hernia. Like osteoporosis, the disease is caused by a violation of mineral metabolism, resulting in weakening of bones and joints.
Why does osteochondrosis appear?
Although traditional medicine considers degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs of the cervical vertebrae to be a disease, from the point of view of osteopathy, it is only a manifestation of deeper disorders in the body.
Thus, the real causes of cervical osteochondrosis are:
- Muscle spasms. . . Spasmodic reactions of the muscles of the back, chest, press can cause certain parts of the body to become very tense. As a result, the general balance of the body is disturbed, causing a change in the position of the spine. Deformities can cause osteochondrosis of the chest, neck and spine by touching the neck or other parts of the spine.
- Poor posture. . . Scoliosis, flexion, back pain, kyphosis and other postural disorders, even small ones, cause severe imbalance of the spine. As a result, the load is unevenly distributed to the intervertebral discs, leading to their deformation and increased wear. The vertebrae begin to converge, causing disruption of nervous processes, cervical osteochondrosis develops very quickly. Postural disorders caused by changes in the natural position of the ribs have similar results.
- Innervation disorder. . . Decreased sensitivity of nerve roots leads to pathological changes in their structure, as a result of which the displacement and deformation of the cervical vertebrae are ignored by the patient. After all, there is no pain due to sensitivity disorders.
- Diseases of the internal organs. . . Improper positioning of internal organs, displacement and lowering due to various dysfunctions cause a general imbalance in the body. As a result, it dramatically affects the condition of the spine - the cervical spine is displaced and deformed, leading to the corresponding types of osteochondrosis.
- Disruption of blood supply. . . Because the spinal discs are not directly connected to the circulatory system, they receive nutrients from the surrounding tissues. Disruption of the blood supply to the cervical spine leads to rehydration of the discs (restoration of shape due to moisture absorption), insufficient fluid intake to regenerate cartilage tissue. As a result, their wear is accelerated, the distance between the vertebrae of the cervical spine is reduced, causing osteochondrosis.
Stages
The attending physician should determine the degree of development of cervical osteochondrosis based on the history as well as the patient's examination. There are only four degrees:
- First degree. . . The disease is in the bud, the patient has a slight pain in the neck, the person begins to turn his head, it may be stronger.
- Second degree. . . The patient may complain of severe pain in the cervical spine, which can be localized in the upper extremities. The clinical picture shows that at this stage of the disease there is compression of the nerve endings, which causes severe pain. Headache, weakness and general malaise are also noted.
- Third degree. . . The pain is almost constant and also spreads to the shoulder or arm. Some patients are diagnosed with a disc herniation, which causes loss of sensation in the upper extremities. There is a significant decrease in the mobility of the cervical spine during the doctor's examination, there is pain on palpation.
- Fourth degree. . . At this stage of the disease, the intervertebral disc is almost completely destroyed. Connective tissue appears in its place, which worsens the patient's condition. He begins to feel more pain, noise in the head, as well as poor orientation in space. This indicates that the artery is constricted, which prevents the brain from feeding naturally.
The first signs
How osteochondrosis of the cervical spine manifests itself:
- radicular syndrome - a pain that spreads from the neck to the shoulder blades, forearms, covering the anterior wall of the chest, against the background of compression of the nerve endings;
- muscle weakness in the arms, noticeable swelling in the neck;
- a characteristic crunch is heard while moving his head;
- weakness, chronic fatigue, decreased blood pressure;
- lack of coordination, often dizziness, attacks are accompanied by nausea, vomiting;
- impaired vision and hearing, noise, ringing in the ears;
- harmony of limbs, tongue;
- frequent migraines;
- Women between the ages of 45 and 65 experience pain during sleep, numbness, tingling in the upper extremities, and attacks may recur several times a night.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Significant symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are dizziness, headache, increased blood pressure.
The disease is difficult to diagnose, the pain is sometimes invisible and the symptoms disappear, and the uncontrolled use of strong analgesics masks the symptoms of the disease. The patient, who does not feel pain, considers himself healthy, and this continues until the development of irreversible processes in the tissues of the neck joints.
Headache with cervical osteochondrosis
The most common causes of headaches in the pathology we describe:
- Vascular spasms of the brain;
- compressed nerve roots;
- Reflex increase in intracranial pressure.
It is felt that the pain can be paroxysmal, constant, throbbing and dull.
Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis
Dizziness can be caused by:
- Inflammation of the middle or inner ear;
- Vascular spasms of the brain;
- disorders in the transmission of nerve impulses;
- problems with the vestibular apparatus;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
There are no clear criteria for dizziness in osteochondrosis. However, there are systemic and non-systemic vertigo, there are obvious differences between them.
It is recommended to know the differences between systemic and non-systemic dizziness, which will help to independently determine the causes of the unusual condition:
- Systemic dizziness - a feeling of circular movement of the surrounding objects or body as a result of disruption of the vestibular apparatus, vision analyzers and receptors in the joints, muscles and epidermis (osteochondrosis of various etiologies);
- Non-systemic dizziness is a feeling of dizziness, a feeling of confusion, not being sure that you are in an upright position. In the case of non-systemic dizziness, there is no sense of circular rotation, and this is a significant difference between the symptoms being compared.
A person experiencing dizziness in one of these types should consult an experienced physician, primarily a neurologist or (in case of suspicion of ear and nasopharyngeal diseases) otolaryngologist.
The reason for emergency hospitalization, which is not associated with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, is that the patient (excluding dizziness) has the following symptoms:
- Paralysis of the facial muscles and numbness of part of the shoulder girdle;
- Severe headache against the background of deteriorating health;
- Impaired coordination of movement;
- Loss or loss of consciousness.
Blood pressure in cervical osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis has long been associated with increased blood pressure. The cervical vertebrae have significant nerve endings and blood vessels.
A distinctive feature of high blood pressure in cervical osteochondrosis is a combination of the following symptoms:
- Headache;
- Pain in the limbs and chest;
- Decreased sensitivity in the neck area;
- Occurrence of pressure increases after stress, muscle tension, prolonged restless posture and other similar situations.
These symptoms should be considered when hypertension of different origins differentiates itself.
Sudden spikes in blood pressure and rapid deterioration of health are grounds for seeking emergency medical care.
Osteochondrosis syndromes
Osteochondrosis consists of the following syndromes:
- Vertebral. . . It is also called vertebral, which indicates the involvement of bone and cartilage tissue in the pathological process. This causes the following symptoms: restriction of motor activity in the neck, pain when turning it, radiological changes in the image of the cervical spine. Simultaneous appearance of these symptoms is a vertebral syndrome. A similar set of clinical signs is observed in myositis (pathology of muscle tissue), and painful movements are a companion to many other pathologies.
- Heart syndrome. . . Burning sensation in the chest area manifests itself with the appearance of shortness of breath. The person feels a rapid heartbeat, becomes tired and nervous. This picture is also characteristic of cardiac pathology, for example, angina pectoris, coronary syndrome, heart attack. An accurate conclusion about the causes of such symptoms can be made after the patient undergoes an ECG.
- Radicular syndrome. . . The cervical region innervates 8 pairs of nerves, each with roots - where the nerve exits the vertebrae. When they are involved in osteochondrosis, the patient feels a decrease in sensitivity or, conversely - severe pain. There may be numbness in the occiput, whether painful, decreased sensitivity of the tongue, pain behind the ear, in the supraclavicular region. Sometimes there are swallowing disorders, movements in the upper extremities, numbness of the fingers.
Diagnostics
If there are obvious signs of cervical osteochondrosis on the face, the doctor prescribes certain methods to make sure that the diagnosis is correct:
- Radiography of the cervical spine. This method is recommended in the early stages of the disease, but may be useless in advanced forms.
- CT (computed tomography). It allows you to see structural changes in the vertebrae, but it is not possible to determine the size of the hernia between the vertebrae using this method.
- MRT. It is the most effective diagnostic method in the diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis. It is possible to determine the size of the hernia between the discs, as well as their degree of development.
- Your doctor may also order a duplex scan to determine if your arteries are not working properly.
Complications of the disease
What is the danger of cervical osteochondrosis:
- frequent migraine attacks;
- cardiac arrhythmias, atherosclerosis;
- protrusion, intervertebral hernia, vertebral bone growths;
- serious pathologies of the brain;
- narrowing of the lumen of the vertebral artery, which leads to the development of VSD, cerebral hypertension, disability;
- spinal cord injury.
First aid at home with exacerbation of osteochondrosis
Painkillers can be used for severe pain. If analgesics do not provide relief, NSAIDs may be taken.
Often used "distracting" means, such as Pepper Plaster, do not heal, but heat the inflamed area and distract from the pain. In case of edema at the site of inflammation, the patient can take an infusion of herbs or diuretics for 3-4 days. Can osteochondrosis be treated with such methods? These measures are temporary, you need to see a doctor to treat the causes.
How to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
In the early stages of development, osteochondrosis can be treated without medication, it is enough to reconsider the diet, daily routine and do a number of special exercises on a regular basis. Effective treatment of advanced forms of the disease is possible only with the use of various drugs that help stop degenerative changes in the vertebrae.
The complex of therapeutic measures should include physiotherapy - electrophoresis with drugs, ultrasound, magnetotherapy, laser therapy. These methods help to fight pain, inflammation, tissue swelling, improve metabolic processes and blood circulation.
Drug treatment
The main methods of treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are especially effective drug therapy, physiotherapy, massage of the neck and neck area, therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. The main groups of drugs used for this disease include:
| ad | Principle of operation |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). | They reduce pain, help eliminate aseptic inflammation and edema of the damaged nerve root. |
| Drugs that improve the rheological properties of blood and blood flow. | Improves nutrition of damaged nerve roots and improves blood flow to the brain. |
| B vitamins. | Improves metabolic processes in nerve tissue. |
| Muscle relaxants. | These are drugs that relieve muscle spasms. |
| Chondroprotectors. These are glucosamine and chondroitin. | These are drugs that repair cartilage tissue, including damaged intervertebral discs. |
When taking pills for osteochondrosis, keep in mind that the significant effect of drug treatment with pills will be only if you combine it with other methods, including exercise. It should be noted that the attending physician must determine how to treat the stage of the disease and other symptoms.
Many doctors consider injection therapy for cervical osteochondrosis to be effective because it allows the nerve endings to move faster and causes minimal side effects. At the same time, vitamins are best taken in pill form because there is no difference in assimilation, but injections can be painful.
Injections used for treatment:
- intramuscular injections have a general strengthening and anti-inflammatory effect;
- blockades are injected directly into the affected area, which causes a rapid effect.
Ointments and gels for external use
This is the most accessible group of medicines for home use. They are divided into anti-inflammatory, warming and analgesic.
With cervical osteochondrosis, not all ointments are effective, in addition, due to their presence, they are sometimes used unreasonably and without taking into account the characteristics of pathogenesis. It should be examined by a doctor before using any medication.
Exercise therapy
Physiotherapy for cervical osteochondrosis should be performed without acute exacerbations. The greatest effectiveness of this technique is in the recovery period. There should be no discomfort or pain during the execution of the complex!
| Exercise number 1 | Lying on your stomach, put your hands on the ground, lift your head and torso, your back should be straight. Stay in this position for 1-2 minutes. Slowly lower yourself to the ground. Repeat 2-3 times. |
| Exercise number 2 | Lying on your stomach, extend your arms across your body, turn your head to the left, try to touch the ground with your ears, then turn your head to the right. Repeat 6-7 times in each direction. |
| Exercise number 3 | In a sitting position, bend forward while breathing and try to touch your chest with your head, then inhale, bend back and bend your head back. Repeat 10-15 times. |
| Exercise number 4 | While sitting, put your palms on your forehead, press your palms to your forehead and your forehead to your palms. Continue this exercise for 30 seconds. Repeat 2-3 times. |
| Exercise number 5 | Slowly turn your head first in one direction and then in the other. 10 rotations in each direction. Look for dizziness. When it appears, the training stops. |

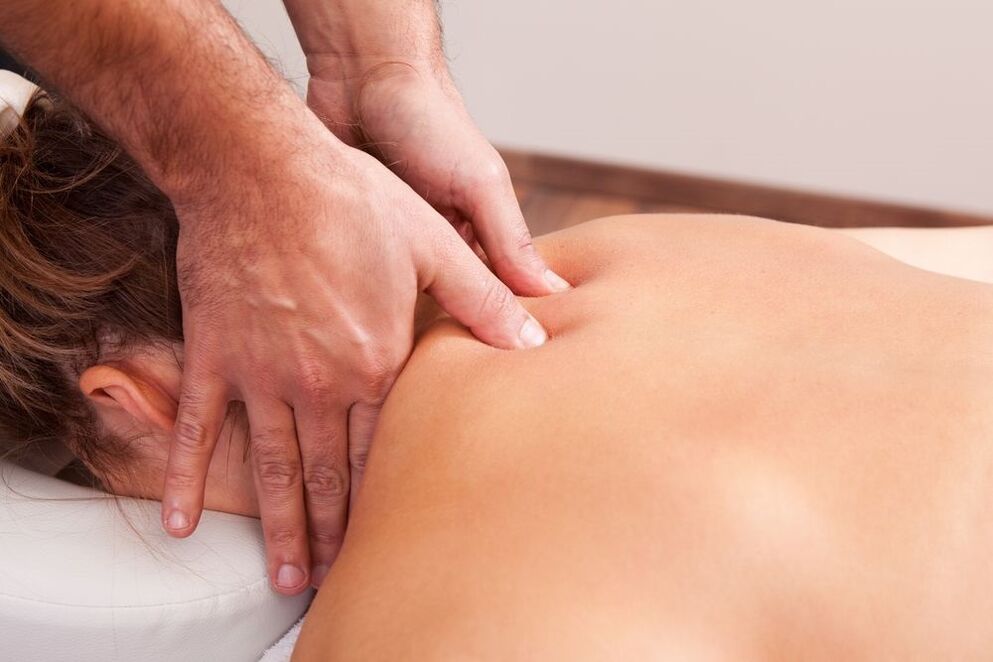
Massage for cervical osteochondrosis
The massage should be done carefully without using force. Inexperienced, unprofessional massage can fail. The movements should extend to the cervical region, neck area and back. The massage is performed in a prone position, in extreme cases, in a sitting position.
The techniques are based on the following techniques:
- Squeeze. Effects on the surface layers of the skin. From the palms of the hands or the tips of the fingers to the upper third of the middle of the lower back. Strokes under the neck can also be zigzag;
- squeezing. Affects the deeper layers of the skin in the upper third of the back. Fingers (thumbs and forefingers) along the neck make movements to catch the skin, reminiscent of squeezing. This is done carefully, the tissues close to the vertebrae are not involved;
- Trituration. The purpose of the procedure is to warm the skin and increase blood flow to the neck. This is done with extreme caution. It is not allowed to affect the spinous processes of the spine. Friction can be replaced by movements reminiscent of a saw or a circular stroke;
- Kneading. It is of limited importance because it affects very deep underlying tissues, which can aggravate the pathology.
Self-massage for cervical osteochondrosis is performed while sitting in a comfortable position. Compression, circular rubbing on the neck or shoulders is used. It is recommended to combine self-massage with rubbing in various ointments that increase blood flow and relieve pain in the kneaded area.
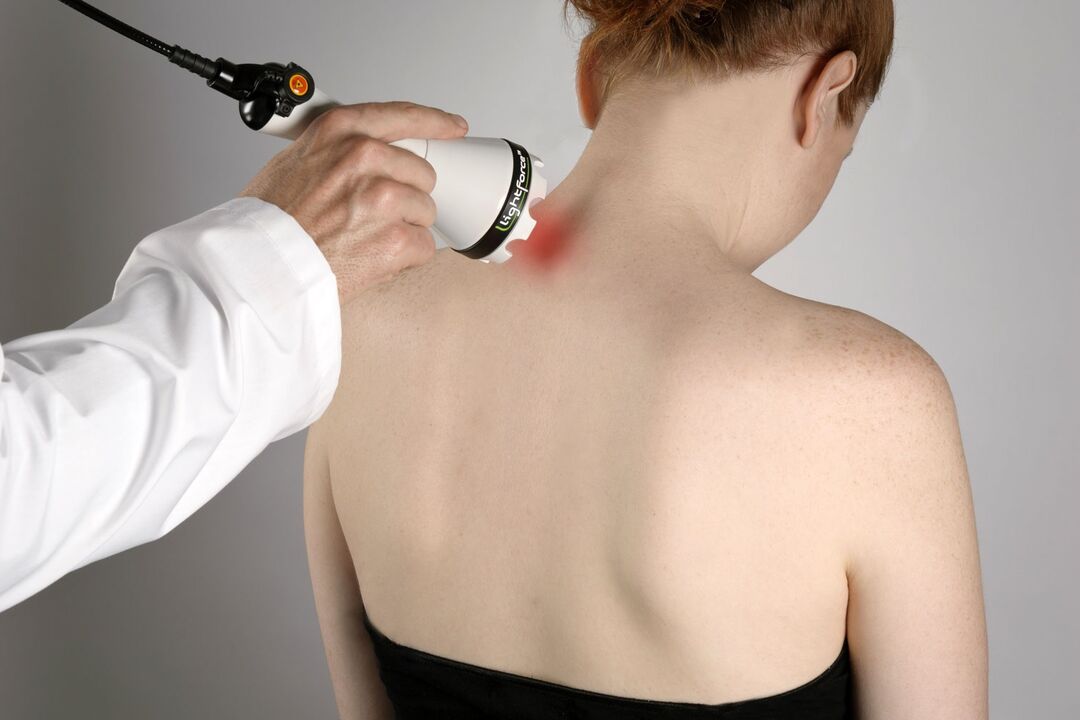
Physiotherapy
In addition to taking medication, the patient must undergo physiotherapy procedures. They increase the effectiveness of medications and help restore joints and intervertebral discs.
- Electrophoresis - the ions of the anesthetic drug penetrate the painful area under the influence of an electric current.
- Laser therapy - has anti-inflammatory properties, guarantees improvement of blood circulation by exposure to light.
- Magnetic therapy - eliminates swelling of tissues, has an analgesic effect.
- Ultrasound - improves metabolic processes, relieves pain, eliminates inflammation of damaged areas.
Several procedures are used in the form of physiotherapy. The doctor prescribes treatment based on the indications and the absence of contraindications.
Folk remedies
Alternative treatment should be used in addition to medication and physical education, as non-traditional methods will not help to get rid of the disease completely.
What to do with cervical osteochondrosis at home:
- Pour boiling water over fresh horseradish leaves, cool slightly, wrap around the neck, flatten with a thin natural cloth. The procedure is performed before bedtime, leave the compress overnight.
- Grate raw potatoes, mix with hot liquid honey in equal proportions. Use the mixture for compresses, the procedure should be performed 1-2 times a week.
- Mix raw egg with 100 ml of sunflower oil, 20 ml of vinegar and 20 g of flour, remove the mixture in the dark for 48 hours, remove the film from the surface. Remedies to stain the inflamed area before going to bed, keep in the refrigerator.
- In May, collect pine buds up to 2 cm long, cut into thin slices and fold into a dark glass jar. Take 2 parts of sugar for 1 part of raw material, leave the drug in the dark for 2 weeks. Drink 5 ml of the mixture three times a day, do not swallow immediately, keep in your mouth for 2-3 minutes. Course duration - 15-20 days, repeat 2-3 times a year.
- Grind 150 g of peeled garlic and 400 g of cornel, put the mixture in a glass jar, after 24 hours add 800 ml of honey and mix. Take 5 ml three times a day before meals.
Cope with severe pain, remove excess salts with a cabbage leaf smeared with honey, tighten the compress around the neck with a warm scarf, leave overnight.
Applicator
The use of applicators is one of the therapies for diseases of the spine, including osteochondrosis.
The effect of the device on the cervical spine normalizes metabolic processes, relieves pain, increases muscle tone, improves blood circulation, increases the permeability of nerve tissue, etc.

Manual therapy
Manual therapy is based on the principle of restoring motor function and mobility between the vertebrae.
At first, the manipulations consist of a light relaxing massage, then the doctor applies more and more force, moving on the vertebrae by pressing and rotating the neck.

Surgery
The spine is the basis of the entire human body. When any pathology related to the spine is diagnosed, specialists try to eliminate it therapeutically. Any operation on the spine is life threatening.
Surgery with cervical osteochondrosis is allowed under the following symptoms:
- intervertebral hernia, spondylolisthesis, spinal stenosis;
- absence of therapy results when exposed for more than six months;
- formation of osteophytes.
Modern medicine offers many methods for performing surgery with minimal risks to the patient's health and life.
Prophylaxis
Cervical osteochondrosis is a disease that develops primarily with an unhealthy lifestyle. Therefore, disease prevention is a healthy lifestyle.
If it is possible to reduce the risk of developing SHO:
- to exclude provocative factors;
- to exercise regularly;
- do not engage in strenuous physical activity;
- get rid of bad habits;
- try to be as nervous as possible;
- eat straight.
Adherence to preventive measures will help speed up the healing process and eliminate the possibility of relapse. Older people and people with hereditary predisposition are always advised to follow prophylaxis. Following a diet and doing simple exercises will definitely give positive results. Yoga and swimming are also helpful.



















